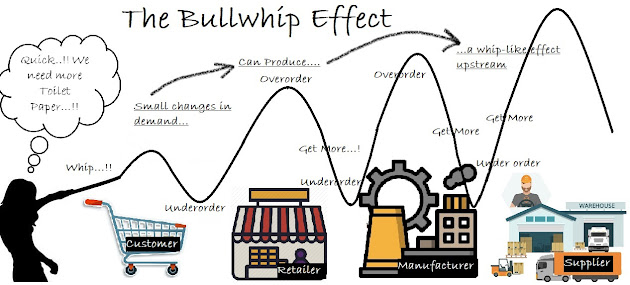
In today’s interconnected and fast-moving global economy, supply chain efficiency is paramount. Yet even the most advanced systems can fall prey to a persistent problem: the Bullwhip Effect. This phenomenon, where small fluctuations in consumer demand cause increasingly larger variations in orders up the supply chain, can lead to excess inventory, lost revenue, and disrupted operations.
One of the most cited examples of this effect comes from Procter &
Gamble (P&G). They noticed massive order fluctuations for their diapers
despite steady sales at retail outlets. What they discovered was a classic case
of the Bullwhip Effect – a disconnect between actual consumer demand and
upstream supply chain responses. But this isn't just a P&G issue – it's a
common challenge faced by businesses across industries.
Behavioural Causes
The first theories focusing onto the bullwhip effect were mainly
focusing on the irrational behavior of the human in the supply chain,
highlighting them as the main cause of the bullwhip effect. Since the 90’s, the
studies evolved, placing the supply chain’s mis-functioning at the heart of
their studies abandoning the human factors. Previous control-theoretic
models have identified the following causes:-
1)
The trade-off between stationary and dynamic
performance, as well as,
2) The use of independent controllers
In accordance with the study conducted by Dellaert, Udenio and
Vatamidou (2017), one of the main behavioural causes that contribute to the
bullwhip effect is the under-estimation of the pipeline. In addition, the
complementary bias, (over-estimation of the pipeline), also has a
negative effect under such conditions. Nevertheless, it has been shown that
when the demand stream is stationary, the system is relatively robust to this
bias. In such situations, it has been found that biased policies (both
under-estimating and over-estimating the pipeline) perform just as well as
unbiased policies. Some others behavioral causes can be:
Factors Leading To Bullwhip Effect
In 1997, studies on the bullwhip effect showed that this last was not solely a result of irrational decision making. More than that, this effect seems to find its source because of the rational behaviors of the players within the supply chain’s infrastructure. The factors may be as follows:
1)
Demand Forecast Updating: Companies
often update their forecasts based on incoming orders instead of actual market
demand. During the COVID-19 pandemic, for example, the panic buying of
essentials like hand sanitizers and toilet paper led retailers to place massive
orders. Suppliers, in turn, increased production, only to later find demand
tapering off, causing surplus.
2)
Order Batching: Businesses
often place bulk orders to minimize fixed costs, leading to irregular demand
spikes. For example, Indian FMCG companies often rely on monthly distributor
orders, which can lead to distorted demand projections at the manufacturing
level.
3)
Price Fluctuations and Promotions: Promotional
discounts encourage customers to buy in bulk, causing artificial demand spikes.
E-commerce sales events like Flipkart's Big Billion Days often see sudden order
surges, pressuring upstream suppliers to ramp up inventory – sometimes
unnecessarily.
4)
Rationing and Gaming:
When shortages are expected, retailers inflate their orders to secure more
stock. During the semiconductor crisis, auto manufacturers like Tata Motors
placed exaggerated orders to safeguard their production lines, further
worsening the shortage.
5)
Lack of Communication and
Visibility: Poor information sharing among supply chain partners
leads to assumptions and overcorrections. Many small Indian exporters faced
disruptions due to limited visibility into international shipping and logistics
updates during global lockdowns.
In addition to greater safety stocks, the described effect can lead to either inefficient production or excessive inventory, as each producer needs to fulfill the demand of its customers in the supply chain. This also leads to a low utilization of the distribution channel. In spite of having safety stocks there is still the hazard of stock-outs which result in poor customer service and lost sales. In addition to the (financially) hard measurable consequences of poor customer services and the damage to public image and loyalty, an organization has to cope with the ramifications of failed fulfillment which may include contractual penalties.
Moreover, repeated hiring and dismissal of employees to manage the demand variability induces further costs due to training and possible lay-offs. The impact of the bullwhip effect has been especially acute at the beginning stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, when sudden spikes in demand for everything from medical supplies such as masks or ventilators to consumer items such as toilet paper or eggs created feedback loops of panic buying, hoarding, and rationing.
Coping With The Bullwhip Effect
1) Collaborative Forecasting and Demand Planning
Leveraging shared data and analytics can align stakeholders across the supply chain. Reliance Retail has implemented AI-driven forecasting tools to better align store-level demand with production, minimizing overstock and stockouts.
2)
Smaller, More Frequent Orders
Encouraging smaller and more frequent orders helps reduce the batching effect. Companies like Amazon India incentivize vendors to replenish stock weekly instead of monthly to create a smoother demand pattern.
3)
Stabilizing Prices and Reducing Promotions
By avoiding frequent price changes, businesses can foster steady buying behavior. Patanjali Ayurved maintains consistent pricing strategies across its products to avoid spikes in inventory orders.
4)
Information Sharing Platforms
Implementing ERP systems and real-time dashboards improves transparency. Infosys’s supply chain platform enables clients to track end-to-end logistics, reducing guesswork in inventory planning.
5)
Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
In a VMI setup, suppliers manage the inventory levels for retailers. Marico has adopted VMI practices with key distributors, helping streamline inventory flows and reduce demand distortion.
Key Takeaways
1) The Bullwhip Effect is not just a technical
glitch in logistics but a reflection of underlying human behavior patterns such
as fear,
overcompensation, miscommunication, and lack of trust.
2) It is driven by psychological tendencies:
panic buying during uncertainty, herd mentality during promotions, and risk
aversion in order planning.
3) Addressing the Bullwhip Effect involves
aligning human decision-making with data-driven insights. This means
fostering collaboration, improving transparency, and reducing emotional
reactivity to short-term signals.
4) Real-world solutions like collaborative
forecasting, vendor-managed inventory, and steady pricing work best when built
on a foundation of trust, empathy, and accountability among stakeholders.
5) By recognizing the behavioral roots of supply
chain inefficiencies, organizations can move from reactive firefighting to proactive
resilience-building, turning uncertainty into opportunity.
Content Curated By: Dr Shoury Kuttappa






Comments
Post a Comment